How to Make Windows More Energy Efficient at Home

Table of Contents
- Why Energy-Efficient Windows Matter
- Energy Loss Through Windows
- Key Features of Energy-Efficient Windows
- Choosing the Right Materials
- Installation Best Practices
- Simple Ways to Improve Existing Windows
- Benefits Beyond Savings
- Real-Life Examples
- Conclusion
Why Energy-Efficient Windows Matter
Maintaining a comfortable home throughout the seasons requires more than simply adjusting the thermostat. Windows are a significant heat and cooling loss source, directly impacting overall energy efficiency. In fact, the U.S. Department of Energy reports that up to 30% of residential heating and cooling energy can be wasted through inefficient windows. Modern solutions, such as replacement windows Rhode Island homeowners trust, paired with professional installation, can dramatically cut energy loss, create a cozier environment, and help lower utility costs.
Homeowners looking to lower their energy costs and improve their living environment often find that upgrading windows is one of the most impactful projects. Energy-efficient windows not only improve comfort but also support a more sustainable household with reduced carbon emissions and resource consumption.
Energy Loss Through Windows
Understanding the routes of energy loss is key to making informed upgrades. Windows lose energy through three main processes: conduction (heat transfer through the window material), convection (air leaks around sashes or frames), and radiation (passing heat energy through window glass). Single-pane windows are especially inefficient, but even standard double-pane options installed decades ago may not meet today’s efficiency standards. Checking for drafts or condensation can help reveal problem areas that need attention.
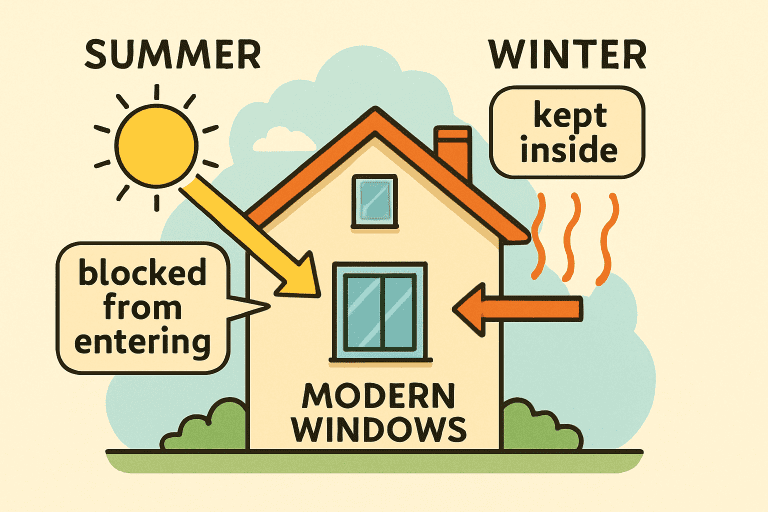
Key Features of Energy-Efficient Windows
Not all windows perform the same. Newer energy-efficient windows boast double or triple glazing, with insulating gas fills like argon or krypton sandwiched between glass layers to slow thermal transfer. Low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings minimize winter heat loss and reduce summer heat gain without sacrificing natural light. Frames also matter: insulated vinyl, fiberglass, or composite frames offer better thermal resistance than bare aluminum.
To ensure you choose high-performance windows, look for certification labels such as ENERGY STAR, which verifies a product has passed stringent energy efficiency guidelines. For more on certification and how to read window performance labels, the National Association of Home Builders’ guide to choosing energy-efficient windows provides detailed comparisons.
Choosing the Right Materials
Frame material significantly influences a window’s performance throughout the year. Vinyl windows are popular for their affordability and low maintenance, providing sound insulation in most climates. Wood frames offer excellent insulating properties and a classic look, but require regular upkeep to deter rot and weathering. Fiberglass and composite frames balance strength, longevity, and resistance to temperature swings, often making them a top choice for energy-conscious homeowners.
Installation Best Practices
Even premium windows fall short without correct installation. Gaps or improper fitting can lead to drafts and leakage, undermining efficiency gains. Professional installation typically includes careful sealing with caulk and weather stripping, sill pan flashing to prevent water damage, and precise shimming to ensure each unit is plumbed correctly and square. If you’re considering DIY replacement, follow the manufacturer’s instructions meticulously and verify your home’s specific requirements.
Simple Ways to Improve Existing Windows
- Apply weather stripping or caulking to seal gaps and prevent drafts.
- Install thermal curtains or insulating window films to slow heat transfer and improve temperature regulation.
- Add storm windows for an extra insulating layer in colder months.
- Use solar shades or blinds to reduce heat gain during the summer.
These affordable steps can deliver immediate energy savings while you plan for more comprehensive upgrades.
Benefits Beyond Savings
Embracing energy-efficient windows provides a host of advantages aside from trimming your energy bill. For one, they often create a quieter indoor space by reducing outside noise—especially helpful if you live near busy roads. Newer windows limit drafts and temperature swings, contributing to better indoor air quality and greater comfort while reducing exposure to dust and pollen. Additionally, government incentives and rebates may help offset initial costs, making these improvements accessible to more homeowners.
Learn more about available energy efficiency incentives and rebates through the Energy Saver program by the U.S. Department of Energy. This program is regularly updated with new resources and initiatives for residential upgrades.
Real-Life Examples
Across the country, homeowners have shared how new energy-efficient windows have transformed their living spaces and utility budgets. In one instance, a family living in Rhode Island replaced drafty single-pane glass with double-pane, Low-E argon-filled windows and experienced a 25% drop in winter heating expenses. Similar retrofits in older homes have also reduced summer cooling costs and improved year-round comfort levels. These success stories are a testament to the significant impact that thoughtful window upgrades can deliver.
Conclusion
Optimizing your home’s windows for energy efficiency can significantly boost comfort, lower your utility bills, and contribute to a more eco-friendly lifestyle. Whether implementing simple solutions like caulking and weather stripping or investing in professional replacement window services, the benefits are immediate and long-lasting. With careful material selection, proper installation, and ongoing improvements, any home—regardless of age or style—can enjoy the rewards of advanced window technology.

