How Heat Pump Systems Save Energy and Lower Utility Bills
Key Takeaways
- Heat pumps can reduce energy consumption by up to 60% compared to traditional heating systems.
- Homeowners may save an average of $300 to $1,500 annually on utility bills after installing a heat pump.
- Proper installation and maintenance are crucial for maximizing energy efficiency and cost savings.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Heat Pump Technology
- Energy Efficiency Benefits
- Financial Savings for Homeowners
- Installation and Maintenance Considerations
- Conclusion
Heat pump systems have become increasingly popular for homeowners seeking to enhance year-round comfort while reducing household energy use. By moving heat instead of generating it, heat pumps provide an effective and environmentally friendly alternative to conventional HVAC systems. This approach not only lowers your energy bills but also supports a greener future—especially when installed by trusted Mississauga heat pump experts who ensure optimal performance for local climates.
Unlike gas furnaces or electric baseboards, heat pumps use electricity to transfer existing heat—in or out of your home, depending on the season, making them one of the most efficient heating and cooling options available today. This efficiency translates not just into energy savings but also into noticeable reductions in home utility costs, even as temperatures fluctuate throughout the year. Understanding how these systems work and how they compare to traditional equipment is essential for homeowners deciding on their next home upgrade.
Furthermore, with climate change top of mind, more governments are offering rebates and tax credits to make energy-efficient options like heat pumps accessible to a broader range of families. These incentives, combined with better technology and experienced installation services, have accelerated the shift to energy-smart homes across North America.
Whether you’re considering a heat pump for its lower environmental impact or its potential for substantial savings, learning about proper maintenance and actual case studies can empower you to make the best decision for your household.
Understanding Heat Pump Technology
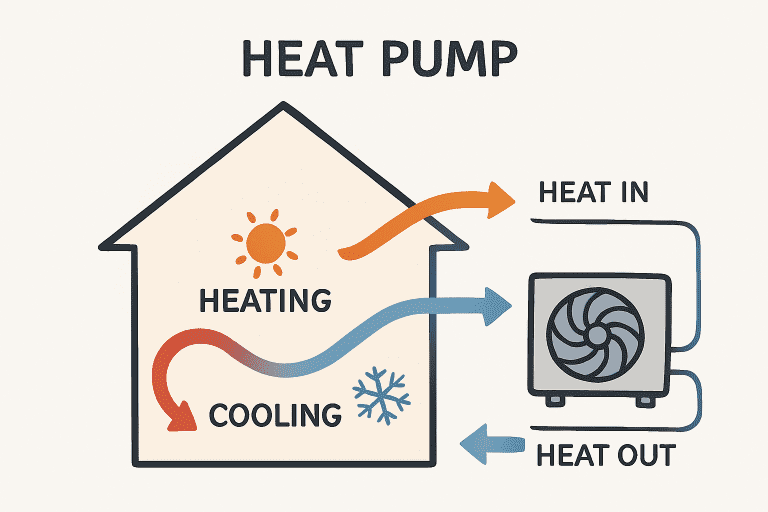
Heat pumps operate on a simple, efficient principle: rather than burning fuel or generating heat directly, they extract heat from the air, ground, or water outside your home and transfer it indoors. When summer arrives, this process is easily reversed to remove heat from your home, functioning as an air conditioner. The core components of a heat pump system—an outdoor unit, indoor unit, refrigerant lines, and a compressor—work together to achieve this heat transfer with impressive efficiency. Because they move heat rather than create it, heat pumps can deliver several units of heating or cooling for every unit of electricity they consume.
Energy Efficiency Benefits
One of the defining features of heat pump systems is their remarkable energy efficiency. Government and industry research, such as that reported by the U.S. Department of Energy, confirms that modern heat pumps can be up to five times more efficient than traditional furnaces and baseboard heaters. This is mainly due to the process of heat transfer, which avoids the energy losses that occur with fuel combustion or electric resistance. When properly sized and installed, a heat pump will maintain your comfort while using far less electricity, reducing your home’s climate impact by cutting greenhouse gas emissions.
Financial Savings for Homeowners
The high efficiency of heat pumps pays off on every energy bill. Households transitioning from oil, propane, or electric resistance heating often realize annual savings ranging from $300 to $1,500, depending on their prior system and typical usage. For example, in Texas, families switching from electric resistance heaters to heat pumps have reported savings averaging more than $300 each year. In contrast, in cold northern states like Maine and Minnesota, savings of up to 60% are being recorded compared to older, less efficient systems. Beyond ongoing savings, the increased value added to your property and reduced maintenance needs further strengthen the investment case for a heat pump. According to US News, homeowners should also consider factors like climate compatibility and installation costs to determine which heat pump system will deliver the best long-term benefits.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Maximizing the efficiency and longevity of your heat pump hinges on professional installation and routine upkeep. Choosing a system that’s correctly sized for your home ensures optimal energy performance and consistent comfort. Skilled technicians can assess your home’s unique characteristics—including insulation, layout, and typical climate exposure—when recommending a system. Once installed, basic maintenance, such as changing filters, checking refrigerant levels, and keeping outdoor units clear of debris, helps sustain peak performance and avoid costly repairs down the line. Most manufacturers recommend at least annual professional servicing to safeguard your investment.
Conclusion
Heat pump systems represent an innovative and forward-thinking investment for homeowners looking to reduce monthly costs while enhancing comfort and sustainability. With key benefits that include significant energy savings, access to lucrative incentives, and minimal ongoing maintenance, these heating systems are poised to play a starring role in the future of home energy management. As more communities and individuals adopt heat pumps and share their experiences, the collective benefits—lower bills, reduced emissions, and better living environments—will only continue to grow.